第七章 Spring Security 中的核心服务
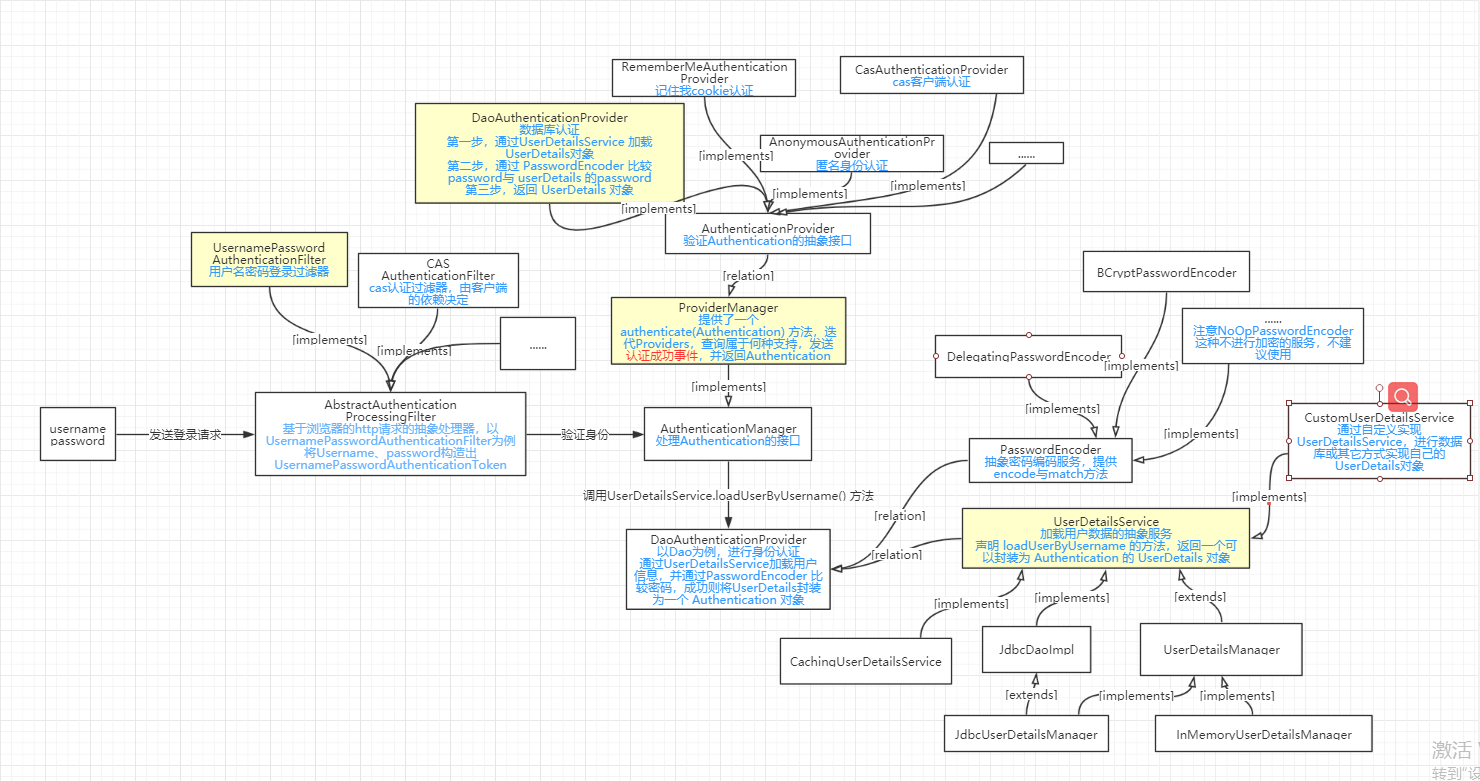
一、核心接口与其实现
在 第五章 SpringSecurity 中的核心组件 与 第六章 SpringSecurity 身份认证流程 中介绍了 Spring Security 体系结构及其核心类。下面更加深入的了解一些核心接口与其实现方法。
上图描述了一个请求认证,大致需要经过的过滤器、接口,及各个接口的子类实现。
其中标黄的部分是下面讲解的重点。
具体的接口与实现类的含义,可以参考官方网站中的解释并结合图中的关系进行梳理。我只会挑选一些核心的实现方法来说。
如果不想看源码,请直接看我写的注释,也能明白这些类的执行过程。
1. UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
拦截并处理用户的登录请求
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
// 1. 登录认证请求必须是POST
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
// 2. 检查请求 request 中是否包含 username、password 参数
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
// 3. 将 username、password 封装为一个 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 对象
// 该对象是 Authentication 的实现类
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
setDetails(request, authRequest);
// 4. 调用 AuthenticationManager 的认证方法
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}2. ProviderManager
上面调用 authenticate(authRequset) 的 AuthenticationManager 是一个接口类,其具体实现是 ProviderManager。当然,也可以选择其他实现类或者自定义。
/**
* 该方法用于验证 authentication(也就是上面传入的 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)
*/
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 1. 循环遍历 AuthenticationProvider 的实现类集合
// 如果有超过一个的 provider 支持,则使用第一个
// 如果一个都不支持,则返回 AuthenticationException 异常
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
// 2. 判断是否支持
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using "
+ provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
// 3. 调用 provider 的认证,下面会以 DaoAuthenticationProvider 为例进行介绍
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
throw e;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
throw e;
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
if (result == null && parent != null) {
try {
// 4. 进行父类的认证尝试
result = parent.authenticate(authentication);
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException e) {
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication
&& (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// 5. 认证完成,请求结束之后,删除 SecurityContextHolder 中保存的 SecurityContext,清除相关数据
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
// 6. 发送验证成功的事件
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
return result;
}
// 7. 身份验证失败,抛出异常
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(messages.getMessage(
"ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() },
"No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
throw lastException;
}3. DaoAuthenticationProvider
DaoAuthenticationProvider 包含两个接口属性 PasswordEncoder 与 UserDetailsService,通过 UserDetailsService 加载用户数据,并使用 PasswordEncoder 比较 UserDetails.password 与 token.password 是否相等。
以此来决定是否认证成功。
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
// 调用 UserDetailsService 的 loadUserByUsername 方法,查询装载 UserDetails
// 在实际开发中,通常会自定义 UserDetailsService 的实现,例如将数据库查询的 User 对象与 UserDetails 对象进行一个适配
// 适配者也需要我们自己定义,如 CustomUserDetails 实现 UserDetails,并将 user.role 转换为 authority等。
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}4. UserDetailsService
UserDetailsService 是整个 Dao 认证框架的核心,用来装载特殊的用户数据。
因为该类为接口类,只声明了一个 loadUserByUsername(String) 方法,所以这里我们使用自定义实现来演示在日常开发场景中的使用过程:
// 1. 实现 UserDetailsService 接口,自定义获取用户的方法
@Service
public class DemoUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
// 2. 注入数据库查询实例,这里不限数据库,只要能获取到用户即可。自己new的也行
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 3. 从数据库中查询到 User 对象
DBUser user = userService.findUserByUsername(username);
if(user == null){
throw new AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundException("user not found.");
}
// 4. 将 DBUser 包装为一个 UserDetails 对象,并将 user.roles 转换为 Authority
return User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder().username(user.username).password(user.password).authorities(user.roles);
}
}二、其他
上面几个类大致说明了,如果将数据库的用户转换为 Spring Security 支持的 Authentication 对象的。
其它如内存认证、jdbcDaoImpl 的实现不再赘述。
还有如自定义 PasswordEncoder、自定义 UserDetails 等其它实现,就不一一列举了,网上一搜一大把。